Good Soil means Good Vegetables, and they give Good Health
We need good vegetables to be healthy. Soil health is essential for human health. to feed our cells with good nutrients. How do we get nutrients? The minerals that our bodies need are in rocks. Can we eat rocks? Of course not. Nature has a system to change the minerals we need into a form that our bodies can make use of. That’s why we have plants to benefit our bodies for our human health and that of the animals we may choose to use as food.
How are Rocks Broken to Form Soil?
Soil formation is a complex process that involves the breakdown of rocks and minerals through physical and chemical weathering. Physical weathering occurs when rocks are broken down by the action of water, wind, ice, or other natural forces. For example, water can break down rocks by causing them to freeze and expand, leading to cracks in the rock’s surface. Wind can also cause physical weathering by carrying small pieces of rock away over time. Chemical weathering happens when chemicals interact with the minerals in rocks, changing their composition and causing them to break apart. This process often results in new compounds such as clay particles that eventually become soil. The soil then continues to be shaped by things like erosion and sedimentation until it is ready for plants to grow in it.
What is Your Soil Like?
This is what we call the ground that we walk on. But is all ground equal? No, not at all. We need good live soil to get the nutrients into our plants and that is how the minerals get into our bodies. Dirt without life will not work for us.
The Loss of Soil Health
Soil health is an important factor in the sustenance of life on this planet. It serves as a medium for growth of plants, and provides essential nutrients to them. Unfortunately, soil health has been deteriorating over time due to deforestation, over-farming and unsustainable agricultural practices. As a result, our soils are now less fertile and have decreased organic matter content. This has caused yields from crops to decline significantly, leading to food insecurity in many regions around the world. Furthermore, erosion of topsoil has caused much of it to be lost forever. This further degrades soil quality and reduces its ability to hold water or other vital nutrients for plant growth. The loss of soil health can also lead to increased risk of drought, flooding and other natural disasters that can devastate entire communities. Therefore, it is essential that we take immediate action to restore soil health by adopting sustainable agricultural practices such as crop rotation, reduced tilling and improved land management techniques.
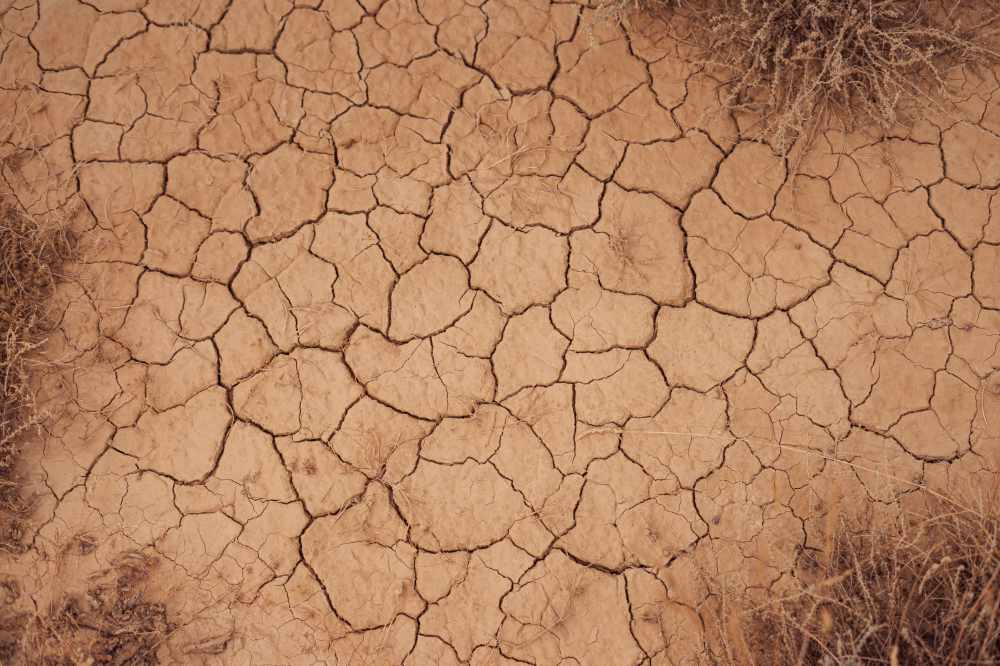

What is in poor soil?
Poor soil is soil with a low nutrient content and poor structure. There are some nutrients, but not in a form that living things can use. It typically has a high clay content, which impedes the proper drainage of water and air, leading to low oxygen levels in the root zone. Poor soil can also be acidic or alkaline, making it difficult for plants to absorb nutrients. Common problems associated with poor soil include low fertility, erosion, compaction and waterlogging.
What causes Soil Degradation?
Soil degradation is caused by a variety of factors, including poor land management practices, over-cultivation, deforestation, overgrazing, and climate change. Poor land management practices can lead to soil erosion, compaction and loss of soil fertility. Over-cultivation leads to nutrient depletion and soil compaction. Deforestation reduces the amount of organic matter in the soil which affects its ability to retain water and nutrients. Overgrazing decreases vegetation cover which increases the risk of wind and water erosion as well as nutrient loss. Climate change can also cause soil degradation through increased temperatures, reduced rainfall, increased intensity of storms and extreme weather events such as floods or droughts which can all affect the health of soils. In addition to these factors, human activity such as mining or urban development can also contribute to soil degradation.
It is a growing concern, that the practice of tilling the soil causes problems, such as disrupting the web of life in the ground and erosion.
What Are Results of Soil Degradation?
Soil degradation is a serious environmental issue that can have serious consequences. It occurs when soil is depleted of its essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and other minerals, or when it is damaged by physical or chemical processes. The result of soil degradation can be severe land degradation, reduced crop yields, erosion and sedimentation, increased flooding and drought, desertification, and even health issues for people living in these areas. Moreover, climate change can also be one of the consequences of soil degradation due to changes in the hydrological cycle. Additionally, it can lead to loss of biodiversity due to reduced habitat for animals and plants. All in all, soil degradation has far-reaching effects that can affect human lives and the environment at large.
Why are Artificial Fertilizers Bad for the Soil?
Man applies artificial fertilizers to the ground, usually in unbalanced amounts. The plants do not use all the the fertilizer that year and the excess ends up running into the creeks and streams. It also “burns” the living things needed to bring the minerals into the plants, therefore “killing” the soil. This disrupts the essential environment needed to support life in the soil.
What is in soil?
Dirt, or soil, is a complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, air and water. The minerals can include sand, silt, clay and gravel, while the organic matter is composed of decaying plant material. Air and water are essential components of dirt, as they are necessary to provide the oxygen and moisture needed for plants to grow. Essential nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorous are also present in dirt. In addition to these components, other elements such as calcium, potassium and magnesium may be found in smaller amounts. All together these elements form a balanced composition that creates an ideal environment for plants to thrive in. Soi is an important resource that provides us with food and other valuable resources. Therefore it is essential to take good care of our soil so that we can continue to reap its benefits for generations to come.

Why is Healthy Soil Better for You?
Healthy soil is much better than poor soil for a number of reasons. To begin with, healthy soil is better at retaining moisture and nutrients that plants need to grow, meaning that less water is needed to keep plants healthy. Additionally, healthy soil has more organic matter, which helps create air pockets in the soil that allow oxygen and other essential gases to reach the roots of plants. This improves their ability to absorb these important nutrients and water. Moreover, healthy soil is alive and contains beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi that can help break down organic matter into usable nutrients for plants. Finally, healthy soil can better hold onto pollutants like pesticides and fertilizers, reducing runoff into surrounding areas. All in all, it’s clear why having healthy soil is so important; its benefits are undeniable!
What Happens in a Healthy Soil?
A healthy soil will function as a vital living thing and is essential for sustaining life on Earth. It contains a variety of organic and inorganic components, including minerals, soil microorganisms, air, water, and decaying organic matter. We see the importance of soils that are healthy, are capable of retaining and storing water and nutrients, which allow plants to grow. The organisms in the soil help to break down organic matter into usable nutrients for plants.
If we build a healthy soil, it can lead to a better water quality as good soil will retain moisture and the water will filter down through the earth’s filtering system. Holding water is proof of a living ecosystem that sustains plants.
Additionally, healthy soil provides habitats for beneficial insects, like pollinators, and animals that can help maintain balanced ecosystems. Healthy soils also store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere which can help reduce global warming. Good soil structure conservation practices will generate better soil. All these functions make it clear why having a healthy soil is so important to the health of our planet!
How Do the Minerals Get into the Plants?
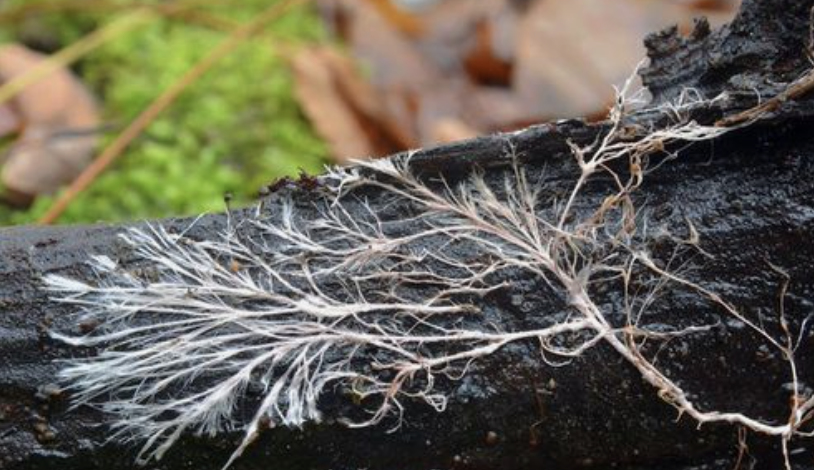
Some of the minerals in soil are Potassium, Iron, Magnesium, Sulphur and Calcium. So how do these minerals get into the plants? The Earth’s system uses a living web of Fungi roots, (mycorrhizae) underground, that connects the plant roots together.
The Fungi and the Bacteria work together to absorb the minerals from the surrounding organic matter that they decompose.
The hunters of the Fungi and bacteria are Protozoa and Nematodes. They eat them and their excretions are now in a form that can be absorbed by the roots of the plants.
All of this life exists right there where the nutrients are available to the plants. The roots of the plants can now absorb the waste products of the creatures.
Animals and humans eat the plants that are full of the nutrients and minerals that we need to thrive.
Soil Science – the Soil Biology
A microbe is an important part of the soil ecosystem. It is part of the Soil Biology. It refers to the microscopic organisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and nematodes that live in soil. These organisms are responsible for a variety of processes including nutrient cycling, decomposition of organic matter, and production of root exudates. They also play a role in disease suppression by competing with pathogens for nutrients and space. The diversity of soil microbes is essential to maintaining healthy soils. Soil management practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic matter additions can help enhance the microbial population and increase the fertility of soils. In addition to providing essential nutrients for plants, these microbes also regulate processes such as carbon storage and water cycling which are essential for sustainable agriculture.
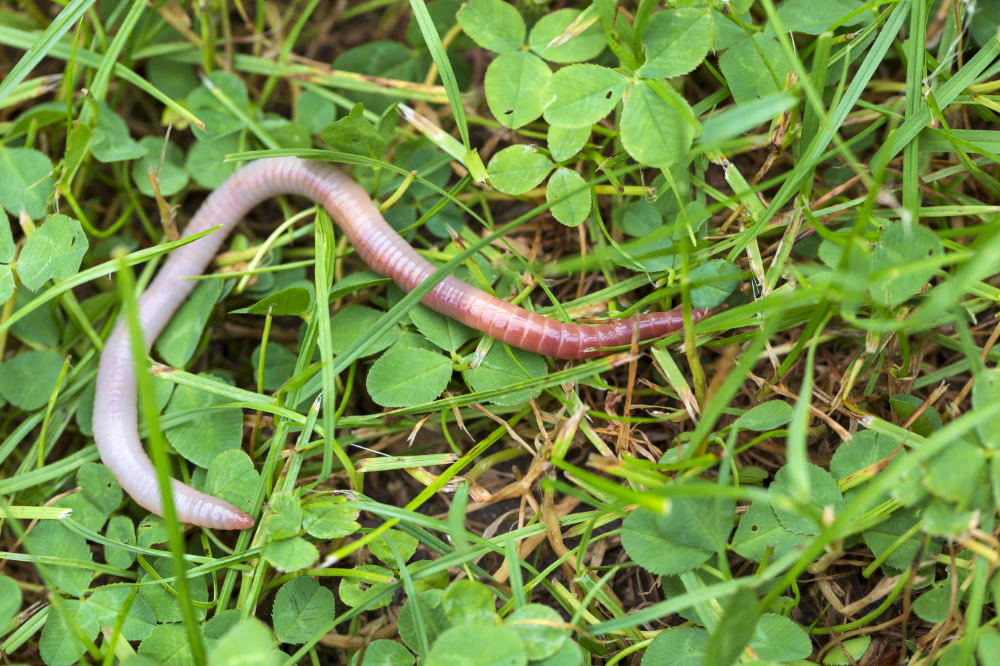
How Do Worms Help the Soil?
Earthworms are undoubtedly one of the most important creatures when it comes to soil health. They play an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter, allowing nutrients to be released and absorbed by plants. Earthworms are also known for their tunneling activity, which aerates the soil and helps maintain its structure. By creating these tunnels, they increase water infiltration and drainage, which can reduce runoff and erosion. In addition, earthworms consume large amounts of organic matter, making them beneficial for composting and nutrient recycling. Their castings contain beneficial bacteria and fungi that help break down nutrients in the soil, making them available to plants. Overall, earthworms are incredibly important for maintaining healthy soils and ensuring proper plant growth.
Management Practices to Improve Soil Health
Soil management practices that promote soil health are key for sustainable agriculture and the production of healthy food. Good management practices include no-till farming, cover crops, crop rotation, composting, and mulching. This practice protects the soil and retains moisture.
Tilling exposes the mycorrhizae root webs in the soil and thus kills the creatures living there. This delays plant growth as the biome of the soil needs time to be rebuilt. No-till farming reduces soil compaction and increases organic matter content by minimizing disturbance. Enhancing soil with a cover crop adds diversity to cropping systems, increase soil fertility, and prevent erosion and improve soil health over time. Crop rotation helps break pest cycles by planting different varieties of plants in the same field year after year.
Build healthy soil by composting, this adds important nutrients to the soil while improving its structure and texture. To improve poor soil, amendments such as compost or manure should be added to increase its organic matter content. Mulching helps retain moisture in the soil and protects it from wind erosion. Each of these principles is essential for increasing the health of soils and should be taken into account when developing a farm or garden management plan.
In Conclusion
Good soil means good plants, so the better you care for the soil, the more nutritious the plants that grow there are. Good soil will increase the productivity of the garden. With soil conservation we can have a better global food system. The more nutrition in your foods, the better your health will be and how you feel.